About ZanVision

ZanVision specializes in optoelectronics and infrared sensing technologies, delivering high-quality image processing solutions for border surveillance, critical infrastructure protection, UAV detection, and other security-focused applications. To meet the challenges of real-world environments, we continuously optimize infrared image quality through a combination of advanced algorithms and hardware acceleration, enabling superior visual performance in complex scenarios.
This article provides an overview of how image histograms are applied in infrared imaging, followed by a detailed explanation of implementing Histogram Equalization (HE) on FPGA hardware. It highlights how algorithm–hardware co-design significantly enhances the visibility and usability of infrared images.
1.Fundamentals of Image Histograms: Understanding Pixel Distribution
An image histogram is one of the most essential and fundamental features in image processing. It represents the frequency distribution of pixel intensities and serves as the basis for numerous enhancement and segmentation algorithms.
1.1Binary Image Histogram
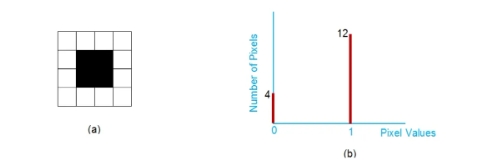
Description: X-axis represents pixel values (0/1), and the Y-axis represents frequency.
1.2 Grayscale Image Histogram
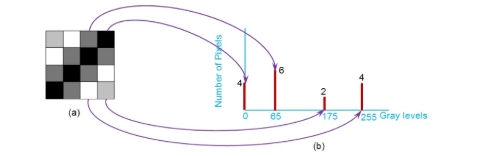
The grayscale range extends from 0 to 255. This is especially important for infrared images, which typically use grayscale representation.
1.3 Color Image Histogram
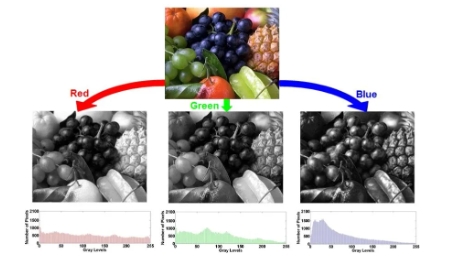
Each color channel (R/G/B) has its own histogram, enabling applications such as color balancing, correction, and multi-channel analysis.
2.Typical Applications of Histograms in Image Processing
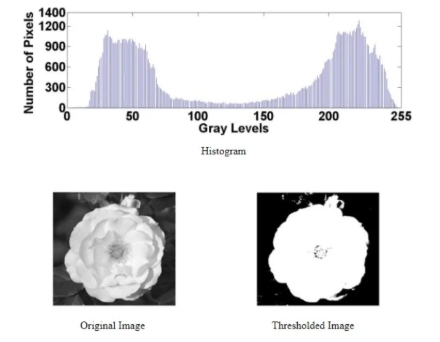
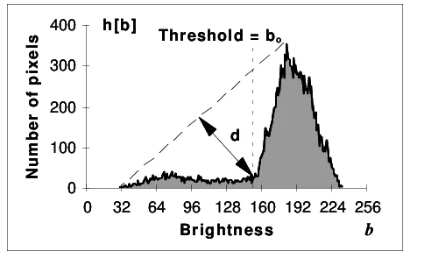
2.1Thresholding (OTSU / Triangle)
Histograms enable automatic threshold selection, supporting foundational tasks in object detection and segmentation.
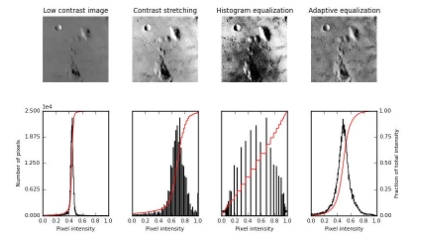
2.2 Image Enhancement: Histogram Equalization (HE)
Histogram Equalization improves the visibility of low-contrast images and is widely used in infrared enhancement.
Common implementations in OpenCV include:
- Global Histogram Equalization
- CLAHE (Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization)
2.3 Image Similarity ComparisonBy evaluating histogram shapes, similarity metrics such as Chi-square, Correlation, or Bhattacharyya Distance can be computed.
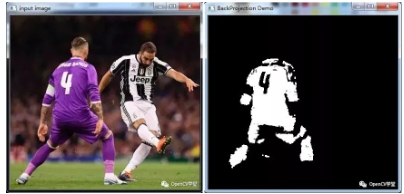
2.4 Histogram Back Projection
Used for target localization and forms the core technique behind MeanShift/CAMShift tracking algorithms.
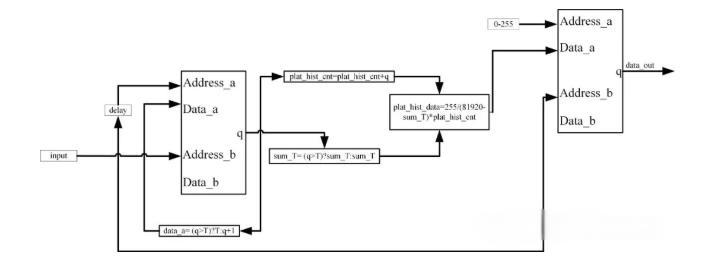
3. FPGA-Based Implementation of Histogram Equalization for Infrared Imaging
Histogram Equalization plays a critical role in real-time infrared image enhancement. Compared with software-only approaches, deploying HE on FPGA leverages hardware-level parallelism to deliver high-throughput and stable processing performance. FPGAs excel in latency-sensitive applications such as high-speed video streams, and their deterministic architecture enhances overall system reliability. As a result, FPGA acceleration has become a standard component in modern infrared imaging systems.
Although the underlying mathematical principles of HE remain consistent, implementing the algorithm on FPGA requires careful redesign of dataflow and memory structures to suit hardware characteristics. The complete pipeline typically includes:
- Image data acquisition
- Pixel-level histogram accumulation
- Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) computation
- Generation of the HE lookup table (LUT)
- Output of the enhanced image
All key modules are implemented in Verilog and executed in a pipelined, parallelized manner inside the FPGA to meet real-time performance requirements.
Our implementation is based on the Altera FPGA development kit from PrimeCore (Zhengdian Atom), using Quartus for hardware synthesis and layout, and ModelSim for functional simulation. Simulation results validated the correctness of the histogram and mapping modules, while on-board testing further demonstrated significant improvements in overall contrast for infrared imaging under real-world conditions.
Enhancing Infrared Imaging Through Algorithm–Hardware Co-Design
Histogram-based techniques remain indispensable tools in infrared image processing. From classical Histogram Equalization to advanced similarity analysis and back-projection algorithms, they play essential roles across a wide range of application scenarios.
By deploying these algorithms on FPGA and other hardware platforms, ZanVision delivers higher real-time performance, improved stability, and superior image quality—empowering mission-critical applications such as border security, industrial inspection, and UAV detection with enhanced visual intelligence.